emissions solutions
explainer: what is carbon capture, utilization, and storage?
2 min read | may 18, 2022
new energies
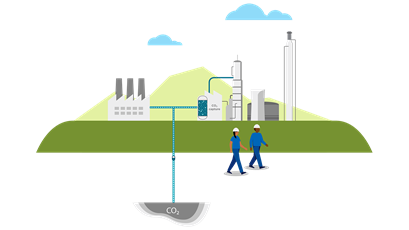
Carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) is the process of capturing carbon dioxide emissions and either using them to make things such as building materials (utilization) or permanently storing them thousands of feet below the surface (storage).
Capturing carbon dioxide from industrial operations before it has a chance to enter the atmosphere helps reduce emissions, as does removing it directly from the air. The carbon dioxide is then reused or sent through an injection well deep underground where it is locked away safely and permanently.
It’s a straightforward concept that takes infrastructure and policy considerations to implement, and Chevron is committed to making it work.
why CCUS is important
CCUS helps reduce the carbon intensity of industrial operations and is a critical component of meeting the global net-zero ambitions of the Paris Agreement.
In fact, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change notes in its Global Warming of 1.5 °C report that achieving net-zero emissions by 2050 isn’t possible without ambitious mitigation actions that could include large-scale deployment of carbon dioxide removal technologies like CCUS.
Because we are committed to advancing a lower carbon future, Chevron is deploying CCUS to lower the carbon intensity of our existing assets and growing our CCUS business targeting third-party emitters as partners and customers. We already have some projects underway with more to come.
that sounds good, but is it safe?
Short answer: Yes.
We know this because large-scale injection and storage of carbon dioxide (CO2) has been working safely and effectively in oil and natural gas operations.
- Safe transportation: CO2 is an inert gas that is not flammable. In smaller amounts, as in CO2 used in carbonated beverages, it can be transported in trucks, and larger amounts of compressed CO2 are usually transported through pipes.
- Safe storage: To store CO2, we carefully select sites within rock formations over half a mile underground. We then store that CO2 underground in depleted oil or gas fields or saline formations. Most sites have an impermeable cap rock that acts as a seal to contain the CO2 permanently.
- Safe reuse: Captured carbon can be put to many uses, from the manufacture of industrial materials, such as concrete, plastic and foam, to clothes and even diamonds.
what we’re doing
We’re using our capabilities, assets and customer relationships to help us become a CCUS leader and develop and scale a CCUS business from start to finish in the following ways:
- We operate Gorgon, one of the world’s largest carbon capture and storage projects.
- We are investing in CCUS technologies and running technology programs on our existing assets with the goal to reduce capture costs to help scale.
- We support academic partnerships that research the advancement of CCUS.
- We’re working to establish storage hubs so nearby customers in industrial sectors can store CO2 to help meet their lower carbon goals.
topics covered
related content
-
 explainer: what do we mean by hard-to-abate industries?
explainer: what do we mean by hard-to-abate industries?emissions solutionsmay 03, 2024
-

 laying the foundation to realize carbon capture’s potential
laying the foundation to realize carbon capture’s potentialemissions solutionsmarch 27, 2024
-

 hydrogen facility to be a chevron first
hydrogen facility to be a chevron firstour operationsfebruary 29, 2024
-

 supply chains are part of the evolution in energy
supply chains are part of the evolution in energyemissions solutionsjanuary 11, 2024
chevron email updates
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive news and updates.



